Gateway¶
Primary function of Gateway is to provide access to remote devices communicating with different protocols. Gateway connects to these remote devices and to the Event Server and serves as the intermediary between remote devices and other components. Once a remote device sends a message to Gateway, it will send the appropriate Event registration request to the Event Server. The same logic is applied in reverse - Gateway sends a message to a remote device once the Event server creates an appropriate Event. With this functionality, Gateway provides bidirectional translation between communication protocols and Event Server’s events.
Running¶
By installing Gateway from hat-gateway package, executable hat-gateway becomes available and can be used for starting this component.
usage: hat-gateway [-h] [--conf PATH]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--conf PATH configuration defined by hat-gateway://main.yaml (default
$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/hat/gateway.{yaml|yml|toml|json})
Overview¶
Gateway functionality can be defined according to following components:
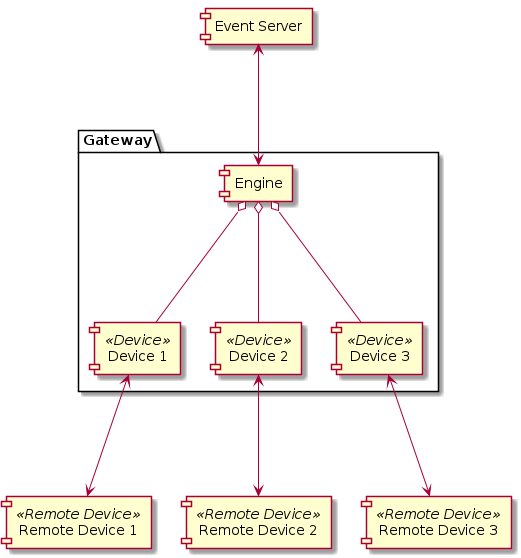
Functionality is dependent on active connection to Event Server. Engine is created when connection with Event Server is established and destroyed if this connection is closed. If connection with Event Server is closed, Gateway will repeatedly try to establish new connection with currently active Event Server. If connection to Monitor Server could not be established or is closed, Gateway terminates it’s process execution.
Gateway can also run independently of Monitor Server. In this case, Gateway connects to predefined Event Server address. If this connection could not be established or is broken, Gateway terminates it’s process execution.
When connecting to Event Server, Gateway will use client name
gateway/<name> where <name> represents configured component’s name.
Event Server communication¶
Communication between Event Server and Gateway is based on Gateway’s requests for event registrations and Event Server’s notification of newly created events. Additionally, Gateway can query previously registered events persisted by Event Server.
All events, consumed and registered by Gateway’s request, have event type prefixed with:
gateway/<device_type>/<device_name>/<source>/...
where:
<device_type> - device type identifier
<device_name> - device name identifier
<source> -
gatewayfor events registered by Gateway andsystemfor events registered by other components
While establishing connection with Event Server, Gateway subscribes for events that match:
gateway/<device_type>/<device_name>/system/*
where <device_type>/<device_name> are all configured devices.
All devices, regardless of device type, support following events:
gateway/<device_type>/<device_name>/system/enable
source timestamp - optional timestamp when component issued event register request
payload - JSON payload encoding boolean value which represents device’s enabled status
gateway/<device_type>/<device_name>/gateway/running
source timestamp - required timestamp when Device is successfully created (started) or destroyed (stopped)
payload - JSON payload encoding boolean value set to
truewhen Device is successfully created (started) or destroyed (stopped)
All other Gateway events are specified in dependence of <device_type>.
Engine¶
Central part responsible for device orchestration. It is created when new connection with Event Server is established and destroyed when connection is closed. It’s main responsibility is managing lifetime of devices and providing custom device’s interface to event server.
Device lifetime is dependent of last enable event state. During
initialization, engine registers a new running events with payload false,
queries last devices’ associated enable event and keeps monitoring for any
new enable events. When device is enabled, engine creates new instance of
device. Once device is successfully created, engine registers new running
event with payload true. If at any time device is disabled, engine will
destroy associated device instance and continue waiting for new enable event.
When device is successfully destroyed, engine will try to register new
running event with payload false. Once engine is destroyed, all devices
are also destroyed.
Device¶
Devices provide abstraction for mapping custom communication protocols to Event Server’s events. Event mapping is uniquely defined according to each device type. Implementation of device logic interfaces with other devices and Gateway’s core logic so additional care should be taken during device implementation (Gateway doesn’t provide sandbox environment for execution of device logic).
Devices available as part of hat-gateway package:
Implementation¶
Documentation is available as part of generated API reference: